- Diabetes has two different forms (Type 1 and Type 2).
- Type 2 is the most common ailment because it can arise from making terrible lifestyle decisions.
- There are 14 early indications of Type 2 diabetes that people should watch out for.
The condition may be treated and prevented from developing into Type 2 diabetes if discovered when it is in the prediabetes stage.
Over 415 million individuals worldwide are thought to have diabetes.
This long-term illness affects how the body converts food into energy. Diabetes prevents some people from making enough insulin or from using it appropriately. However, if you are diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes at an early enough stage—the prediabetes stage—you may be able to alter your lifestyle to slow the development of full-blown diabetes. Only if you know the early warning signals of Type 2 diabetes are early diagnosis and behavior adjustment possible.
What Is Diabetes Type 2?
Even though there are two forms of diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2), Type 2 is significantly more prevalent, particularly in more industrialized nations. More than 90 to 95 percent of all people with diabetes in the country have Type 2. A genetic disease called type 1 diabetes often manifests in childhood. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes can develop at any stage and is frequently linked to lifestyle decisions.
In those with type 2 diabetes, the body cannot produce enough of the essential hormone insulin, which helps control blood glucose levels. Medication is frequently required for Type 2 diabetics to manage their disease. Over time, this condition may also cause heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, nerve damage, eye damage, blindness, problems during pregnancy, sleep apnea, hearing loss, and depression. 2
Type 2 Diabetes’s 14 Early Signs
Those who believe they may be at risk for Type 2 diabetes should look for these 14 early warning signals. Do not forget that a multitude of causes might cause Type 2 diabetes. While the symptoms on this list can be used as a general guide, it’s crucial to note that certain warning signs may be more subtle than others. If you have any concerns about your health, it is always a good idea to speak with your doctor.
1. Growing Hunger
Your blood’s glucose is used by the body to fuel your cells. The cells can’t absorb the glucose they need when the body can’t make enough insulin. The body reacts by increasing appetite when it senses that it isn’t getting enough nourishment. This could lead to a vicious cycle in which you overeat, making the underlying issue worse and worsening your health. It may be wise to see a doctor if you’ve been feeling more hungry than usual.
2. Continual Urination
Your body cannot control its blood sugar levels if it lacks insulin. Your kidneys can’t keep up with eliminating the extra sugar from the body when blood sugar levels are too high. As a result, some sugar enters your urine and causes you to urinate more frequently, especially at night. Consider talking to a doctor if your increased frequency of urination is interfering with your sleep cycle to see if the problem may be resolved.
3. Continual Thirst
People with high blood sugar and frequent urination have constant thirst. No matter how much the person drinks, this thirst frequently remains unquenchable. It might be time to see a doctor if you consistently feel thirsty despite drinking plenty of liquids. Always keep in mind to steer clear of sugary beverages because they may exacerbate your problems. Prioritizing drinking water is crucial.
4. Cloudy Vision
People who have diabetes run the danger of losing the clarity of their vision, and some may even go completely blind due to the condition (known as diabetic retinopathy). Vision blur is a Type 2 diabetes early warning indication.
The blood vessels in the eyes may be affected when blood sugar levels abruptly rise—blurring results from fluid entering the eye’s lens. The blurriness usually goes away after a while. Still, if it persists for an extended period, it can be a symptom of trouble.
5. More Exhaustion
It may be a symptom of a health problem if you consistently receive a total of eight hours of sleep yet still wake up feeling exhausted. Because the body uses glucose as fuel, low glucose levels can produce constant exhaustion. Diabetes fatigue syndrome is the term used to describe the relationship between increasing fatigue and diabetes.
Keep a log of your sleeping patterns, the hours you get each night, and how tired you feel in the morning. You may have a problem if you wake up every morning feeling exhausted.
6. Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
Diabetic neuropathy is a disorder where diabetes can occasionally harm the nerves. High blood sugar levels can have this effect because they interfere with normal blood flow, which eventually causes nerve damage. The hands, fingers, feet, and toes may experience tingling, numbness, or discomfort due to diabetic neuropathy.
The majority of people who have diabetes eventually develop diabetic neuropathy. Still, it might be the disease’s first symptom in some cases.
7. Wounds that Heal Slowly
Diabetes patients frequently observe that their wounds heal more slowly. Your blood vessels may eventually get smaller due to high blood sugar levels. This causes sluggish blood circulation and prevents wounds from receiving the oxygen and nutrients they require fast. Even minor wounds and injuries can occasionally take weeks or months to heal.
The body’s diminished capacity to mend will impact any internal wounds or lesions, in addition to the apparent problems brought on by slowly healing flesh wounds. Consult a doctor if healing from minor cuts takes weeks or months.
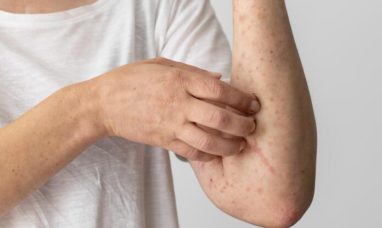
8. Dark Skin Patches
Acanthosis nigricans is a disease that is more common in people with diabetes. Dark areas of skin that feel velvety, soft, and smooth are the outcome of this disorder. The armpit, groin, and neck are only a few places on the body where black spots frequently form. Because diabetes leads to insulin resistance, these dark patches of skin result from too much insulin in a person’s bloodstream. If you’re watching for Type 2 diabetes early warning signals, take some time to glance at your body in a mirror.
9. Often Contracting Yeast Infections
Frequent yeast infections in women can occasionally be an early indicator of Type 2 diabetes. Your kidneys cannot filter everything out when your blood sugar is high. This causes some sugar to wind up in your urine, which frequently causes a yeast infection.
Chronic yeast infections can be a symptom of a significant health problem in addition to being uncomfortable. Contact your doctor if you notice a dramatic increase in the frequency of yeast infections.
10. Skin Itches
One of the initial indicators of diabetes is frequently itchy skin. Diabetes-related disorders, including a yeast infection, a fungal infection, or poor circulation, can all contribute to this itchy skin.
Even though itchy skin is simple to ignore, being aware of it can assist in identifying potential problems. It could indicate something more sinister if you’ve observed that you’re itchier than usual and that scratching doesn’t make the itching go away.
11. Dry Mouth
The majority of people with diabetes experience chronic tongue dryness. Although the exact cause of dry mouth in patients with diabetes is unknown, it is thought that elevated blood sugar levels are to blame. The following signs and symptoms of dry mouth will appear:
- cracked, parched lips
- infections or sores in the mouth
- No matter how much the person drinks, their mouth remains dry.
- difficulties swallowing, speaking, and chewing
- a harsh, dry tongue
12. Intolerance
Many people experience mood swings due to their blood sugar levels’ frequent oscillations between high and low. Because their bodies are attempting to adjust to fluctuating blood sugar levels, people with diabetes are more likely to experience increased sensations of irritation, anxiety, and worry.
This warning indication transcends Type 2 diabetes. Although irritability and mood swings may not directly impact your health, they can cause problems and conflict with those around you.
13. Unintentional Loss of Weight
People with diabetes cannot use the glucose in their bodies as fuel efficiency. As a result, the body will occasionally react by burning fat reserves, which leads to unanticipated weight loss.
Significant weight loss can also lead to several health problems, including feeling significantly weaker than usual. Even if sudden weight loss doesn’t always mean you have Type 2 diabetes, it can be a sign of other medical conditions. This is an unambiguous indication that nothing is amiss. Therefore you should see a doctor immediately.
14. Prediabetes
The majority of patients first experience prediabetes before developing Type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes can manifest with some, but not all, of the warning signs of diabetes. It is not yet a recognized form of the disease. Early detection of prediabetes can be advantageous since it allows the patient to adjust their lifestyle and start taking medication to prevent the condition from worsening.
Your most valuable asset is your health, but it can be vulnerable. To find out what might be causing any symptoms, it’s critical to have them evaluated by a medical practitioner.
Featured Image: Unsplash © Diabetesmagazijn